Introduction to the API Patterns
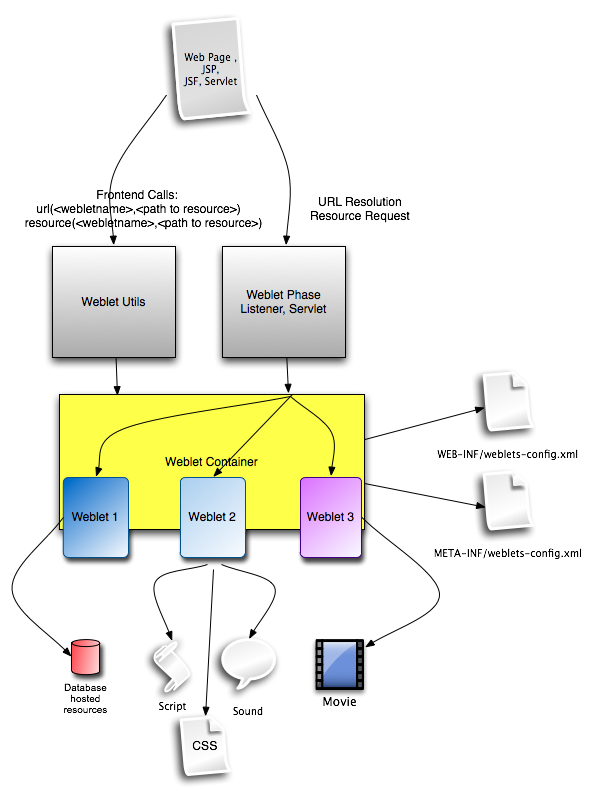
Weblets contain two parts in their execution pipeline, a frontend API , which enables a neutral notation for application developers to isolate the resource call from the actual calling protocol and position. a url resolution stage, which intercepts the actual resource call and serves the resource from a given datasource.
General Functions
The application of those principles is very easy, all the application programmer has to use, is the frontend specific API .
Weblets tries to stay the same as much as possible in its APIs and their results over all frameworks, so that the application programmer can be sure that the final result stays the same, not depending on the underlying framework being used.
The basic idea of the Weblet fronted API, are two contractual functions/methods.
Code 1: Contract Functions/Methods
url(<webletname>,<path to resource>)
resource(<webletname>,<path to resource>)
In every framework supported, you always will find them one way or the other.
The main difference between those two contractual methods is, that url serves up a full url including the current web application context, while resource only serves up the relative path to the resource.
The following code example shows the differences between the two functions.
Code 2: Difference between url and resource in a pseudo API
url ("org.myapp.html","/myresource.js")
resolves to /my-webapp/faces/weblets/myapp/myresource.js
resource( "org.myapp.html","/myresource.js")
resolves to /faces/weblets/myapp/myresource.js
Contents
- Users documentation: Index
- What is new in this release
- Users documentation: Getting started
- Users documentation: Setup guide
- Users documentation: Introduction to the api patterns
- Users documentation: JSP Weblets usage guide
- Users documentation: Servlet Weblets usage guide
- Users documentation: JSF Weblets usage guide
- Users documentation: Resources Weblets usage guide
- Users documentation: Weblets packaging guide
- Users documentation: Weblets Subbundles
- Users documentation: Weblets reporting guide
- Developers documentation: Programming Weblets
- Users documentation: Weblets general FAQ